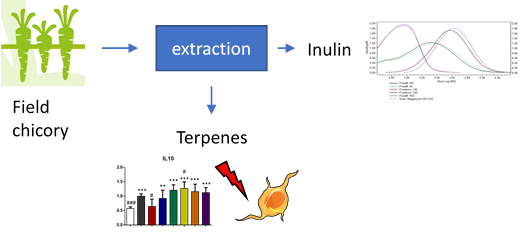
Commercial exploitation of chicory as a multipurpose crop
The aim of WP8 is to collect and analyse the information gathered from other WPs and finally to develop two strong business cases for NPBT chicory, where the other one is related to dietary fibre and the other for bioactive terpenes. Important dietary fibre component in chicory is inulin, which for example promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Inulin is produced in varying lengths in chicory and the longer the inulin chain, the more beneficial it is and less it causes unpleasant gas formation in the intestine. Terpenes, on the other hand, are small natural compounds, which are produced in chicory to compete in the environment and which have beneficial properties for humans, too, for example as antimicrobial compounds or anti-cancer drugs.
In WP8, the NPBT chicory with improved inulin and terpene fractions are studied for they bioactivity as well as for safety. Improved inulin properties will be demonstrated by both inulin structure and chain length and in gut fermentation models, which mimic the conditions in human gut. These studies allow evaluation of the digestibility properties as well as alterations in gut microbiota after inulin intake. The terpenes possessing the most promising bioactivities, will be evaluated for their toxicity to ensure their safety. Exploitation potential of the most promising NPBT chicory variants will be further evaluated via different value chains models for business case development.
Gut fermentation and microbiological models showed that the inulin length influences to gas formation and a slight increase in beneficial Lactobacillus gut bacteria can be seen after inulin intake. Various cell models for intestinal toxicity have been implemented and studies are currently on-going. Two values chains were defined: 1) for both inulin and terpenes and 2) only terpenes. Different food grade solvents for extraction of inulin and terpenes were evaluated and a hypothetical market price was calculated for the terpenes (inulin has a known market with a known market price). For both value chains a terpene market price was calculated that was in range with typical market prices for pharma ingredients, leading to the conclusion that in this phase both value chains appear to be feasible market options.

 This project has received funding from the EU Horizon 2020 research & innovation programme under grant agreement N. 760891.
This project has received funding from the EU Horizon 2020 research & innovation programme under grant agreement N. 760891.